Metal expansion joints—also known as metal bellows expansion joints—are critical components used in pipelines to absorb thermal expansion, vibration, and mechanical movement. To ensure long-term reliability and safety, each expansion joint must be produced with precision-engineered equipment and pass multiple tests before delivery.
This article introduces the complete manufacturing process, the required machinery, and the essential testing procedures.
1. Raw Material Preparation
High-quality stainless steel plates or coils (commonly SS304, SS316L, or special alloys) are selected according to the working temperature, pressure, and corrosion conditions.
Key steps include:
-
Material inspection and certification check
-
Cutting steel sheets into the required width and thickness
-
Surface cleaning to remove oil and contaminants
Main Equipment:
-
CNC plate cutting machine / shearing machine
-
Decoiler and straightening machine
-
Surface cleaning equipment
2. Cylinder Forming (Rolling)
The prepared sheet is rolled into a cylindrical shape, which will become the base tube for the bellows.
Main Equipment:
-
3-roller or 4-roller plate rolling machine
After rolling, the sheet edges are aligned to create a perfect circular tube.
3. Longitudinal Welding
The seam of the rolled cylinder is welded to form a complete and strong tube.
TIG welding (GTAW) or plasma welding is commonly used to ensure high weld quality.
Main Equipment:
-
Automatic TIG welding machine
-
Plasma welding machine
-
Internal backing purge system
After welding, the seam is polished and inspected.
4. Corrugation Forming (Bellows Forming)
This is the core step in producing a circular metal expansion joint. The welded tube is formed into bellows with a series of waves (corrugations).
Available Forming Methods:
-
Hydraulic forming – high-pressure water or oil expands the tube into a corrugated mold
-
Mechanical forming – special rollers mechanically press the corrugations
-
Expanding and rolling combined forming – suitable for multi-ply bellows
Main Equipment:
-
Hydraulic bellows forming machine
-
Mechanical forming machine (rolling type)
-
Multi-ply forming system
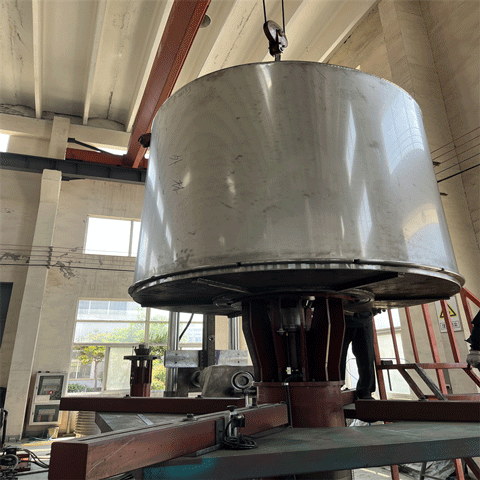
5. Heat Treatment (Annealing)
Bellows are heat-treated to relieve internal stress and improve flexibility and fatigue resistance.
Main Equipment:
-
Continuous annealing furnace
-
Controlled-atmosphere furnace
6. End Fittings Welding Assembly
According to customer requirements, various end connections are welded to the bellows:
-
Flanges
-
Welded ends
-
Threaded ends
-
Pipe spools
-
Tie rods / limit rods (for pressure balance type)
Main Equipment:
-
Welding workstation (TIG/MIG)
-
Positioners and rotary tables
Welds must remain deformation-free to ensure sealing integrity.
7. External Surface Treatment
Depending on application:
-
Polishing
-
Pickling and passivation
-
Anti-corrosion coating
Main Equipment:
-
Polishing machine
-
Pickling tank
-
Spraying booth
8. Required Testing Procedures
To guarantee safety and reliability, each expansion joint undergoes strict tests:
1. Visual & Dimensional Inspection
-
Wave height, wave pitch, total length
-
Thickness measurement
-
Weld appearance check
2. Dye Penetrant Inspection (PT)
Used to detect surface cracks on welds and corrugation areas.
3. Pressure Test (Hydrostatic Test or Pneumatic Test)
-
Hydrostatic pressure test for strength verification
-
Air pressure leak test for sealing performance
-
Usually 1.5× working pressure
4. Cycle Life / Fatigue Test (Optional for OEM orders)
Simulates repeated expansion and contraction to ensure the bellows’ design life.
5. Material Certification and Traceability
Includes:
-
Material test report (MTR)
-
Chemical composition analysis
-
Mechanical property testing
9. Final Quality Control and Packaging
Qualified products are cleaned, dried, protected with plastic film, and packed in wooden cases to avoid deformation during transportation.
Conclusion
Producing metal expansion joints requires advanced forming technology, precise welding, and strict quality testing. With the right equipment—such as hydraulic forming machines, automatic welding systems, and pressure-testing facilities—manufacturers can ensure high-performance bellows that guarantee safety and reliability in pipeline systems.